
MARSApplication cases
NIR-II in-vivo Imaging, that is, near-infrared two-region fluorescence imaging is a new small animal in vivo imaging technology that has emerged in recent years, breaking through the limitations of traditional fluorescence imaging technology, with the advantages of large penetration depth, high spatial resolution, and fast speed, and is known as the next generation of fluorescence imaging technology. Combined with the biofluorescence probe of the infrared region, it can be applied to many studies such as angiography, tumor imaging, organ imaging, lymphatic and lymph node imaging, intestinal microbiota imaging, surgical navigation, pharmacological pharmacodynamic evaluation and drug distribution in vivo.
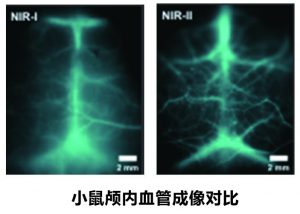
- Compared with the traditional near-infrared first region (NIR-I, 600-900 nm), the fluorescence imaging of the near-infrared second region (NIR-II, 1000-1700 nm) has the characteristics of less tissue absorption, weak light scattering, and low autofluorescence background, and has more obvious optical imaging advantages
- Penetration depth is higher than 15 mm and spatial resolution is better than 4 μm
- Fluorescence lifetime resolution is better than 10 μs and high-speed acquisition speeds above 1000 fps
MARS Technical advantages
High sensitivity
The core camera of the new generation mars system adopts the NIRvana series of the industry-renowned Teledyne Princeton Instruments, which has the advantages of high sensitivity, low noise, and high-speed imaging. Provide high-quality imaging data for various small animal in vivo research projects.
- Liquid nitrogen refrigeration series, as low as -190 °C, suitable for single-molecule ultra-micro fluorescence imaging;
- High-speed series can be up to more than 250 frames per second, suitable for fluorescence life, angiography, surgical navigation, etc.;
Large dynamic range, to achieve strong signal and weak signal simultaneous monitoring, for drug metabolism, tumor metastasis and other research to provide more reliable quantitative analysis
High resolution
The MARS system provides two sets of self-developed high-resolution, high-throughput short-wave infrared lenses: FAST and Pathfinder, which can realize the overall observation of two rats (30×36 cm) at the macroscopic scale at the same time, and can also continuously zoom to achieve accurate analysis on the microscopic scale (600×720 μm).
- FAST: F/#1.4, 50 mm large aperture lens, 900-1700 nm transmittance>90%;
- Pathfinder: Continuous zoom lens with 900-1700nm transmittance >70% and a maximum resolution of <4 μm.
High-resolution near-infrared two-zone in vivo microscope
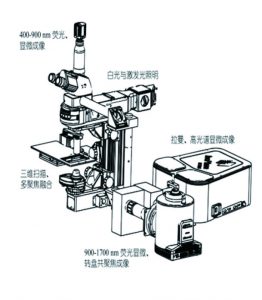
VENUS is the latest full-spectrum imaging microscope with wavelengths ranging from 400-1700 nm. The optimization and design of the optical path for the near-infrared two region can help users obtain microfluorescence imaging of small animals in vivo. Compared with conventional microscopic imaging techniques, NIR two-zone microscopy has the characteristics of deep penetration depth, fast speed, and compatibility with visible/near-infrared one-zone microscopy imaging. It can be used in many fields such as microangiography, in vivo neuroimaging, local fine imaging of tumors, conventional cell staining experiments, pathological section analysis and so on.
The VENUS NIR two-zone microscope is designed for biological low-light experiments and has:
- High sensitivity: 400-900 nm peak QE>95%, 900-1700 nm peak QE>87%;
- High resolution: Visible light resolution is better than 300 nm, NIR-II is better than 700 nm.
- High compatibility: Modular design, easy to inherit confocal imaging, microspectral systems, Raman systems, fluorescence life and other modules. Convenient for users to expand and upgrade.



